Everyone could use a traffic boost. Even if you are satisfied with your visit statistics, you wouldn’t mind a 30% bump, right?
You just need to make your web page more visible in Google’s search results and visitors will gladly come.
So you do the usual stuff: create new content, put keywords everywhere, sprinkle that with a few links to popular websites to add credibility and wait… until you realize that it’s not 2011 anymore and Google is much more sophisticated.
“On-page SEO checklist” is the answer.
See that phrase in quotation marks? That’s my focus keyword and I put it exactly as the 100th word of this article. One of the best SEO practices is to put your main keyword phrase within the first hundred words of the article.
That’s a quick tip right from the start.
In this article, we discuss tips and strategies related to on page SEO techniques. It can be used by people that are just starting their business or by seasoned business people that want to have all the optimization techniques nicely described in one place.
You can print the remaining part of this post as a checklist and hang it near your monitor to ensure that you produce the most optimized content you can.
What is on-page SEO?
On-page SEO (sometimes referred to as ‘on-site SEO) are all efforts that a marketer can do with their website that improve search engines’ understanding of the page’s content and enables better matching between search queries and your content.
A well-optimized web page can get you a lot of free traffic for promoting your offers.
In other words, it’s about readability for search engines such as Google.
As a marketer or content manager you know the concept of readability. It’s a measure of how easy a given piece of content is for a person to read it and understand it. Some techniques that help the content to be more readable include using simple sentences and avoiding passive voice.
Similar logic lies behind on-page SEO techniques. Search engines want to know:
- What a given page is about
- What information it provides
- Is it reputable?
You can do a lot to improve your page’s quality in the eyes of search engines.
On-page vs off-page SEO
To make sure that we are on the same page, let’s talk about differences between on and off page SEO.
If you are doing something with the page, like improving its content or adding keywords to URLs, that’s on-page SEO.
If you are trying to get other websites to link to your page or you ask influencers to promote your content: that’s off page SEO.
Both of these techniques are crucial to get a good spot on the SERP page.

What tools do I need?
Although there are many tools that may help you along the long way of improving your web page’s design, you don’t need anything pricey. Many keyword research tools are free to use, as well as image optimization software for example.
Some example keyword research tools include:
- Wordstream (free)
- Google Keyword Planner (free)
- SurferSEO (paid)
- Keyword Tool (paid)
- Kwfinder (paid)
There are a lot of tools that can help marketers maintain their ad campaigns or build websites. Paid SEO tools are optional for those that really want to take the top spot on the SERP page.
Now, onward with the checklist.
1. Research your keywords
Long gone are the days when all a cooking blogger had to do was to repeat the phrase “Spaghetti Aglio e Olio” fifty times in their recipe to be deemed as the spaghetti expert in Google.
Keyword stuffing no longer works and is actually one of the things that may lower your rank.
But you still need to use keywords.
- Create a list of terms that describe your content’s website first
This may include product features or benefits for ecommerce marketers or article topics for bloggers. If you haven’t created the content yet, check for what your audience is looking for.
Analyze Google trends, use tools such as AnswerThePublic or Quora to learn about pain points of your audience. You have probably done half of the work while researching your audience or searching for the best marketing niche.
- Research these terms in a keyword research tool
Your goal now is to find your main focus keyword that is popular but maybe not so competitive. You want to find one parent keyword and a few child keywords.
Parent keywords describe a general product category on a high level, while child keywords define a narrower niche.
For example, if you sell TV’s, the parent keyword would be something like “oled tv”, while child keyword would be more specific: “65 inch oled for less than $1,000”, “120 Hz gaming oled tv”.
If you use keyword research tools, they will tell you which keyword is which: parent keywords are often referred to as seed keywords or parent topics.
- Find LSI keywords
LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords are thematically related with each other. They are not synonyms. LSI keyword for ‘running’ is not ‘jogging’ but ‘fitness tracker’ or ‘hydration’.
Why go through all the trouble of finding those keywords?
Because this is the way Google learns about the content of your page. As we have said earlier, repeating one keyword a bunch of times is not enough for fooling Google’s algorithm. It searches for words that often coexist together on other web pages on a given topic.
So, if you really want to tell Google that your site is about running, include a lot of LSI keywords.
Where to get ideas for these keywords?
One of the best ways of discovering related keywords is by checking either the Google autocomplete on a given topic or checking the “People also search for” snippet.
2. Make your content readable
This point works both for search engines and people.
It may be a shock for you but most people don’t read your posts from A to Z. They usually skim it to get an idea about your article’s general structure and read only the part that is interesting for them.
Don’t fight it, encourage it. Let them know from initial scan of post that it will answer their questions
- Avoid writing long text blocks
- Use ordered lists or bullet lists for most important points
- Use images, not only for decorative purposes but for the information you want to make visible (like your product’s success rate, positive trends, main threats, and so on).
- Use correctly structured headings (H1 for title, H2 for main headings, H3 and H4 for subheadings)
Additionally, use natural language. Use real-life examples, address the reader directly. Make your content easily digestible.

3. Add keywords to right places
Keywords go into several places, not just in the title and somewhere in the text.
- Include keyword in URL
Try to make your URL as short as possible and put your keyword as far to the left as possible.
Make your URL sound natural, not automatically generated gibberish. URL ‘myblog.com/best-oled-tv’ works better than ‘mblog.com/fsdjhigdg-g455g5544-oled-tv-54gg‘. Some CRMs do that automatically.
Use hyphens in your URL and avoid including session IDs in the URL. This produces a lot of similarly-looking links that don’t look good in Google.
- Include keyword in title
Try to put it as close to the beginning of your title as possible. When your title is too long, it may be cut off in the SERP page and your precious article will end up looking like “The ultimate and no-nonsense guide to getting the best…” instead of “Best OLED TVs in 2022: Ranking”.
A good practice is to divide the title into two parts: one for search bots that includes your keyword, and one for social that invokes curiosity. The two parts are usually separated by a colon.
Look at the example: ‘Best OLED TVs: What companies won’t tell you’
Such a title is easy to read and makes both bots and human readers happy.
- Include the keywords in the SEO title (title tag)
SEO title is the one that is visible in the SERP page, while regular title is the one visible on page load. You can use different titles, for example, SEO title can tell you what the article is about quicker while a regular title can be funny and clever.
- Include keyword in first 100 words of post
Yes, we’ve covered that one in the beginning.
Note that it is often better to put the keyword in the second sentence of the article, not first, because this way it looks less pushy.
- Put keywords in your headings and subheadings
You can also use child keywords if they exist.
- Include keywords in a meta description
Meta description is the summary of your page that will be visible on the SERP page. Make it immediately clear what your page is about and include a keyword.
- Use image alt attribute
Alt attribute or alt text is the description of an image that is not displayed to the visitor but is read by a search engine. Google likes to know what your image contains. If the description of the image includes a keyword, such a page will be seen as more attractive by Google.
4. Optimize images
Images are a fun way of increasing your page attractiveness. Use:
- Decorative images
- Infographics
- Images with bullet points and important sentences
Don’t hesitate to repeat what you just wrote in an image. People read images when they scan text.
Now, when it comes to optimizing images, do the following:
- Make sure that they load fast: compress them without sacrificing quality and store them on a fast CDN. Loading times are an important SEO factor.
- Use alt attribute or title attribute. Use keywords and descriptive text for them.
- Make sure that our images don’t exceed the maximum width of your site layout and that they scale responsively on various screen sizes.
- Use relevant file names.
- Use captions for better experience and readability
5. Optimize headlines
We’ve talked about including keywords in your headlines. Let’s talk some more about making your headlines more appealing to humans and search bots.
Content structure
In HTML, a markup language for documents that are supposed to be viewed in the web browser, headlines are marked as H1, H2, H3, and even H4. They create a hierarchy that structures your content.
H1 is your header, a title that is visible on page load. You should use only one H1 headline per page.
H2 are lower rank headlines that compartmentalize your content into smaller and more digestible chunks. Think of them as chapters to your article.
The number of H2 headlines depends on the lengths of your content. Ideally, you should avoid putting a lot of text without breaking it with some headlines. Too few headlines can lower your rank in Google as Google’s search bot will have a harder time understanding your content and may deem it hard to read.
H3 headlines further divide your content within your chapters. Again, the ideal number depends on the length of the text but a rule of thumb is that you should use a headline every time you start a new topic or an aspect of a given topic.
A clever headline structure makes your content easier to skim read for impatient readers. Help them find information they are looking for as quickly as possible.
Creating a catchy headline
Creating headlines follow the same principles as creating catchy titles. Follow the simple rules below:
- Use numbers. People like numbers and assess the content below the headline or title with numbers as more trustworthy. What’s strange, odd numbers seem to have a bigger effect than even numbers. ‘Top 10’ lists are no match for ‘Top 11’ ones.
- Invoke curiosity or emotion. While numbers appeal to reason, certain words call to our emotional side. You may try to make your readers feel:
- Curiosity: “Easy savings are just 5 clicks away”
- Fear: “Don’t lose money on this fraud”
- Excitements: “Save money and have fun while doing so”
- Use power words. Power words are those that immediately catch a reader’s attention: ridiculous, banned, skyrocket, secret, incredible, unlock
The last thing worth remembering is that a correct headline structure can make your in-text headlines appear on the SERP page. This can further improve your CTR, as more of your page’s content will be presented to people.
6. Optimize meta description
Meta description is your article’s summary that appears on the SERP. You have approximately 155 characters to:
- Tell people what your page is about (shop page, article, guidebook)
- Informs people what is the benefits for them (‘Get the best deal’, ‘Learn everything about…’)
- Inform search engines about your page’s content with keywords
- Stand out from other pages on similar topic
If you use more characters, meta description can get cut off on the SERP page. This doesn’t look nice and fails to deliver the whole message to the reader, so the strong suggestion is to stick to the limit.
Meta descriptions are invitations, write them like one. Use active voice and informal language. If you link to a product page, include the product’s specifications.
7. Optimize for featured snippet
Featured snippet is something that is strongly divisive in the SEO experts community. Some people will do a lot to be included in one, while others don’t particularly care or even don’t want their pages appearing in one.
The general consensus is that being in a featured snippet is a sign of a well SEO-optimized web page.
What is a featured snippet?
Featured snippet is a part of the layout of the SERP. This snippet contains an extract from an article that fits best with a search query.
Featured snippets may contain a sentence or a bullet list from your article. It can even create a list from your numbered headlines.
What are the upsides and downsides of appearing in a featured snippet?
The upsides seem obvious: Your page is even more visible to the user, as it takes a bigger part of the SERP page, and it provides answers to users immediately.
The last part is also the biggest downside.
Users that have already found answers they were looking for may be reluctant to click on your page. Your click-through rate will go down.
-> If you have a CTA button – it won’t be clicked.
-> If you have ads on your site – they won’t be displayed.
What’s best for the user may not necessarily be the best for the web page owner.
But let’s say that you’ve weighed all options and decided that you want to appear on featured snippets.
Optimizing for featured snippet
Make your content digestible for search bots:
- Use lists and bullet points
- Number your headlines.
- Emphasize the most important parts of your page with bolded font or otherwise.
- Provide answers for many similar questions
You won’t get a notification when you get a featured snippet, you have to check it for yourself occasionally.
8. Add links
In the late 90s, when Google was just one of many pages on the infant net, linking was the primary way of understanding a web page’s importance. Google’s creator brought to the Internet the same logic that applied to scholar papers: if many people quote your work, it must be good. Analogically, Google started analyzing the number of links going to and from a web page and deemed pages with the most backlinks (links that direct to the page) the best.

Right now it obviously takes into account hundreds of different metrics but linking still remains one of the most important ones.
Types of links
There are two main types of links:
- External: links that lead to pages outside your domain. If a link goes from a different domain and links to your website, it is called a backlink. If you link to a different website, it is also an external link.
- Internal: these link to web pages under your domain (for example, your other blog posts).
Backlinks are a part of off-page SEO and deserve a separate article. In this post, let’s focus on what you can do on your own website. Let’s talk about outbound links.
Outbound links
The way you link your articles with each other tells Google what the relationships of your pages are. If you link to one of your pages more, it will be seen as more important.
Homepages usually have a lot of links leading to and from them.
Many content managers follow the logic of creating ‘clusters’ of articles on similar topics. They create one main article, usually called ‘cornerstone’ or ‘pillar’ article that is a general introduction to the topic (for example, ‘The ultimate TV buying guide’) with smaller articles on more niche topic linking to the main one (articles such as ‘OLED vs LED TVs: What you need to know’, ‘Best TVs for gamers’).
There are several best practices for creating good links:
- Link to high-quality web pages with reputable domains. These web pages should have content on topics similar to yours. It’s better not to have a link at all than to link to a domain with poor reputation.
- Link to other pages on your blog: older blog posts, concrete product pages.
- Use meaningful anchor text. Anchor text is the clickable part of the link. Avoid using general anchor text such as ‘Click here’. Keywords are important but context of a link is even more important. Don’t just stuff keywords into anchor text, make sure that the surrounding text is relevant.
- Use ‘dofollow’ and ‘nofollow’ links. This attribute is an instruction to search bots to follow or ignore links. You don’t need Googlebot scanning links to your login or contact pages, for example. You want only links that are relevant to the topic of the article scanned.
9. Add schema markup
You may have taken it for granted or didn’t pay much attention to it, but results in Google consist of more than just a link and meta description. Depending on the content type, you may also see information such as:
- Address and phone number
- Movie repertoire
- Restaurant menu
- Product subpages
And so on. This provides a lot more information to the user and takes up more space on the SERP page.
Websites that get such nice listings use Schema markup. It is a result of a collaboration between the world’s biggest search engines (Google, Bing, Yandex, Yahoo) to improve user experience.
Schema markup adds additional scripts that describe the type of content. So the search engine knows that if you mention ‘Avatar’ in your content, you mean the movie, not the image. In the same way you may highlight hundreds of other types of information.
By doing so, you further improve the scannability of your content.
And you can do this automatically.
Just go to the Google’s Markup Helper, direct to your page and use instructions provided there to assign type values to various pieces of content on your web page.
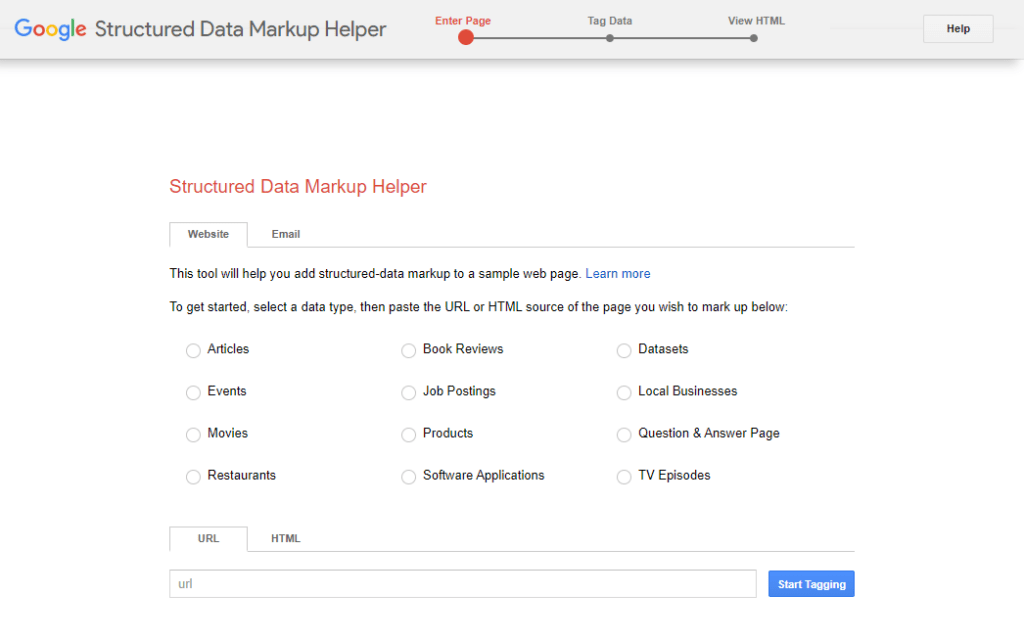
What Google will then do is generate a modified HTML file that contains schema markup scripts. You will then have to go to your CMS or directly to the HTML code and either manually put these scripts into correct places, or simply copy and replace your HTML code with the modified one provided by Google.
This is a serious advantage for you to take, as it turns out that merely 30% use this technique, so it is easy to get ahead of 70% of web page’s content.
10. Maintain the page
Don’t worry, we are nearly at the end of our checklist.
In fact, if you’ve followed all the tips and techniques listed above, your web page is as optimized as it can be.
The last thing to remember is to keep your web page fresh.
Google likes newly updated content. Your readers will also appreciate up-to-date content.
- Keep adding new information even long after the publishing date.
- Make sure that all the links still work.
- Replace stale images.
- Add new links to relevant content that you have created after the publishing date.
- Include information on the date and scope of the update.
Without doing so, you are wasting a lot of time that went into creating this content. Sometimes refreshing old articles may be quicker and more important than creating new posts.
Rank higher with on-page SEO: A handy printout
Concluding statements with a list of the 10 steps:
- Do your keyword research
- Make it readable
- Add keywords to right places
- Optimize images
- Optimize headlines
- Optimize meta description
- Optimize for featured snippet
- Add links
- Add schema markup
- Maintain the page
You’ve spent a lot of time on your page: You took the time to do the research, prepared the content, designed the page, set it up and did all the optimizations. The last thing could take you even more time than all of the previous things combined.
You are now ready to publish your page. Await visitors. See page visit statistics increase.

While this is a nice perspective, there’s still work to be done. There are still off-page SEO methods that may have an immense impact on your site’s view count.
But that’s a topic for another article.
For now, congratulate yourself on creating a well-optimized page. In the eyes of most marketers, this is more important to a web page’s popularity than paid campaigns.
The last thing to do is to connect ad analytics solution such as Voluum and wait for visitors.



One comment
Great article. Will look forward for more such information