Setting up Google Analytics 4 for tracking your pages is far from the hardest thing to do but may not be the easiest. It lays somewhere between conducting a brain surgery and ordering a pizza.
Ordering a brain surgery?
For people that don’t know anything about using Google Analytics 4, we have prepared a GA4 tutorial that will guide readers through the meanders of we analytics.
Despite following the tutorial or even your years-long experience, you may still discover that your analytics don’t work correctly.
The quickest and most general suggestion I can give is to use Google Analytics 4 DebugView to troubleshoot your campaigns.
For concrete answers to typical Google Analytics 4 problems, read below.
1. Missing Demographic Data in GA4
Demographic data, such as age and gender, provides valuable insights into your audience’s characteristics and preferences. Google uses a feature called Google Signals to collect data on users across devices.
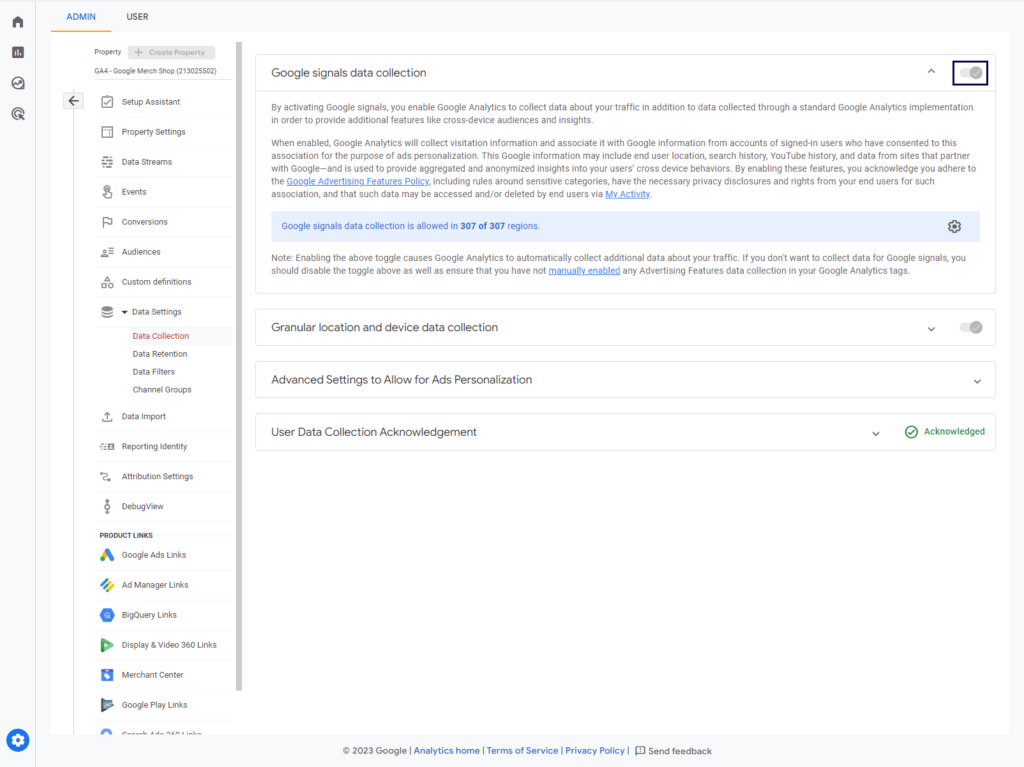
By default, Google Signals is turned off. The simplest thing to fix missing demographic data is to turn Google Signals on:
- Go to Admin
- Select the correct property.
- Got to Data Settings / Data Collection
- Enable Google signals data collection.
The other explanation for missing demographic data is that you haven’t waited long enough. It takes some time for the data to populate your reports. Give yourself a 24 – 48 hour waiting window after setting up analytics.
Also note that you should be getting a significant amount of traffic for Google to track demographic data. If your website gets just a few views per day, don’t expect any demographic data to be collected.
2. GA4 Audiences
Audiences are groups of visitors that share a common characteristic. This may be very general, such as ‘purchasers’ or very specific, such as ‘purchasers from a given city within the last 7 days’. The common problems and solutions with Google Analytics 4 audiences include:
- No data available. Possible cause: Not waiting long enough. Google will start creating audiences after 30 days of collecting data.
- Not being able to create an audience. Possible cause: Reaching the limit of audiences per property. The current limit is 100.
- Parts of data hidden. Possible cause: Thresholds applied. Google applies thresholds to data when Google Signals is turned on and user count is low to prevent you from identifying concrete users.
Audiences can be transferred to other Google properties such as Google Ads. You only need to link your GA4 property to Google Ads. You can do this under one Google account.
3. Scroll Tracking with GA4 and GTM
Tracking user engagement through scroll depth can provide insights into how users interact with your content. BY default, Google Analytics 4 tracks scroll depth with Enhanced Measurements. But it only records the 90% scroll depth.
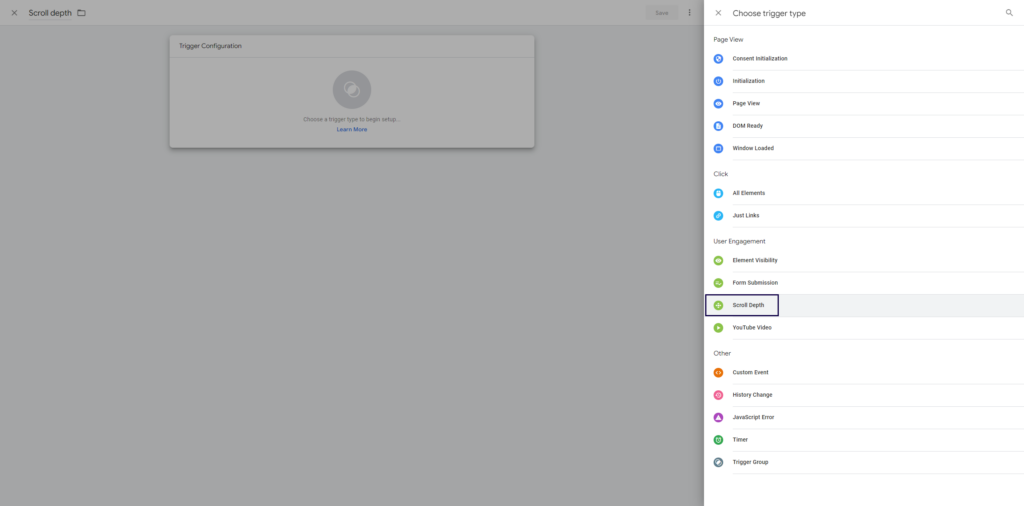
If you want to track other scroll depths, you need to configure a trigger in Google Tag Manager:
Select ‘Scroll depth’ as a trigger in GTM.
Then, set up a concrete scroll depth value.
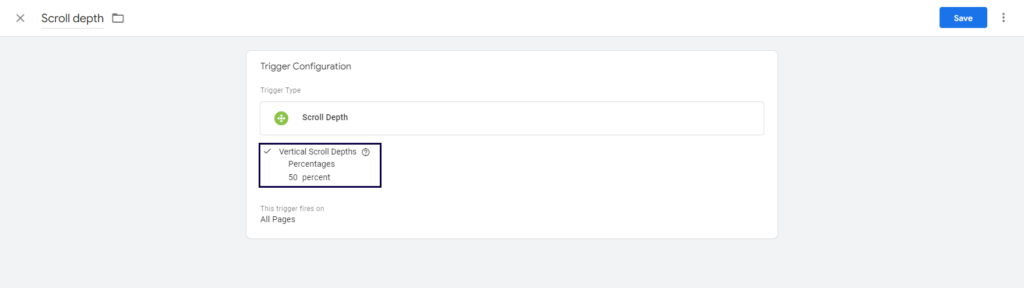
Implementing scroll tracking allows you to understand how far users scroll on your web pages, enabling you to optimize content placement and improve user experience.
4. Duplicate Events Fixing in GA4
Duplicate events can skew your data and lead to inaccurate analysis. There are several reasons for data being recorded twice. Luckily, there are easy fixes for these problems:
- Google Analytics 4 and Google Tag Manager are set to record the same event independently. Solution: Audit your setup.
- Google Tag container has been added multiple times on the same page. Solution: remove unnecessary containers.
- When migrating from UA to GA4, both platforms are set up using Google Tag Manager and record events independently. Solution: Fix your GA4 migration.
By fixing your setup, you ensure that only unique events are counted in your GA4 reports, providing a more accurate representation of user interactions.
5. Exclude Internal Traffic with GA4
When analyzing user behavior, it is essential to exclude internal traffic, such as visits from your team or office, from your data. To exclude internal traffic in GA4, consider the following options:
- Go to Admin / Data streams.
- Select Web stream and click on it.
- Click ‘Configure tag settings’.
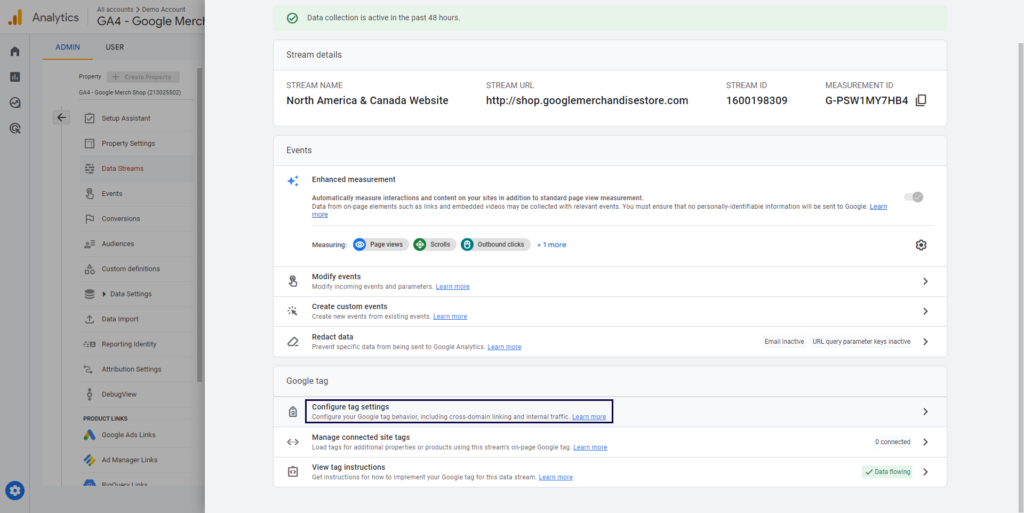
- Click ‘Show all’ and ‘Define internal traffic’.
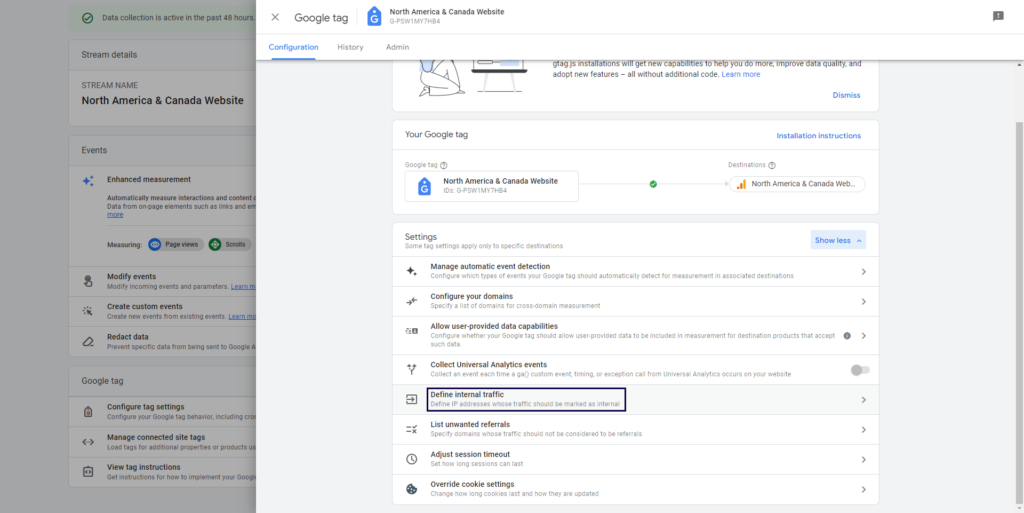
- Click ‘Create;.
- Set up a rule for IP ranges that are behind your internal traffic.
6. Check if GA4 is Working
After setting up GA4, it’s crucial to verify if data is being collected correctly. Follow these steps to check if GA4 is working:
- Install the GA Debugger extension (for Chrome, Firefox, Opera) in your browser.
- Open your website and enable the GA Debugger extension.
- Open developer tools and look for the “Collect” request in the debugger’s console log.
- Verify that the request includes your GA4 measurement ID (G-XXXXXXXXXX).
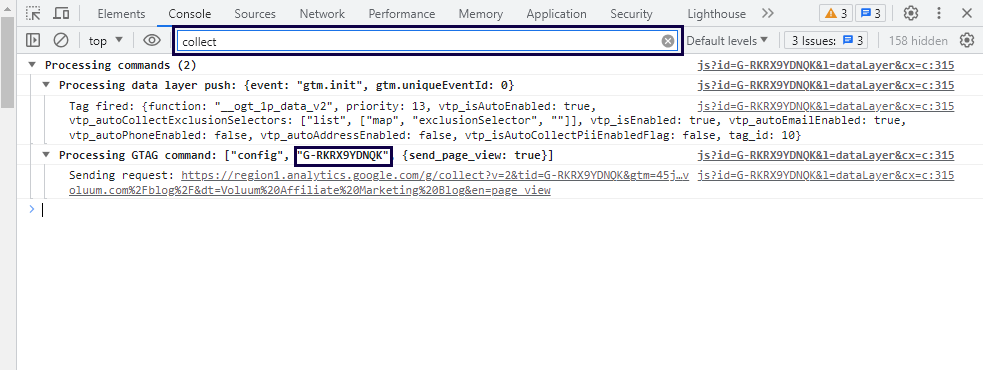
If the request appears with the correct measurement ID, it indicates that Google Analytics 4 is working and collecting data accurately.
7. Find Search Terms in GA4
Understanding the search terms users use to find your website is vital for optimizing your content and SEO strategy. In order to find search terms, you need to have site search enabled first.
Once you have site search enabled, follow the steps below:
- Access your GA4 property.
- Go to the ‘Reports’ / ‘Engagements’ section in the left-hand navigation menu.
- Click on ‘Events’.
- Click on ‘Search terms’.
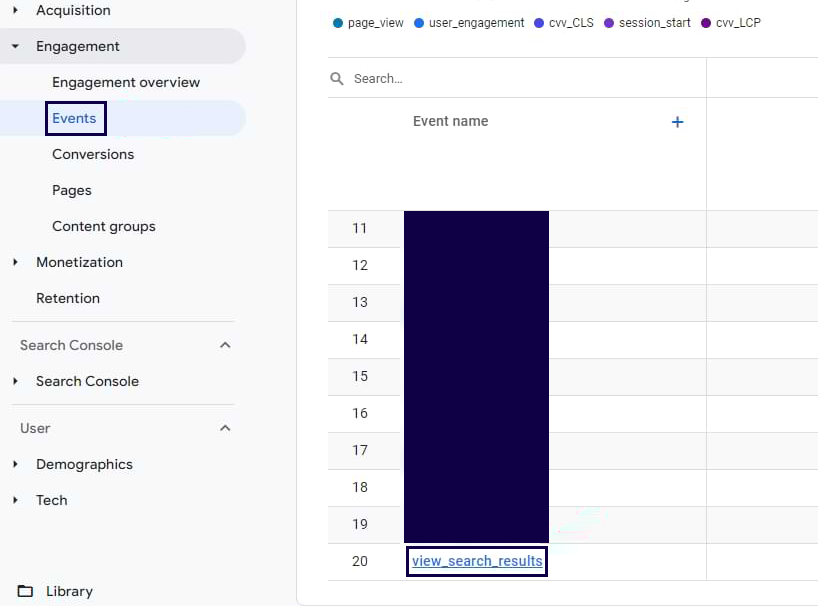
- Analyze the provided search terms report, which shows the terms users searched for on your website.
By identifying the search terms users employ, you can tailor your content to align with their interests and improve organic traffic.
8. Google Analytics User ID for Cross-Device Tracking Setup
Cross-device tracking allows you to understand user behavior across multiple devices, providing valuable insights into their journey. The user ID has to be provided by you – you can generate it using user login data such as email address.
To send User ID data to Google Analytics 4, you need to modify:
- Google tag:
- Find the config command in the measurement code.
- Add the user ID info.
- Your code should look like this:

- Google Tag Manager
- Set up a data layer to push User ID:

- Create a user ID data layer
- Configure your GA4 tag in Tag manager by adding a parameter with this data layer.
By implementing cross-device tracking with the User ID, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of user behavior and create a seamless user experience across devices.
There are alternatives
If this list of common GA4 problems and tricks makes you wish for another ad tracker, we have a proposition for you: try Voluum and you may be astonished with results.
Voluum is a performance ad tracker for paid advertising. It introduces different philosophy to tracking, enabling marketers to perform large-scale test to optimize their campaign funnels. Voluum works in a cloud and supports various tracking methods, such as redirect or pixels, with the latter relying on 1st party cookies instead of 3rd party like Google tracking pixel.
Give Voluum a try and level up your campaigns’ run in a way you never though was possible.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, setting up Google Analytics 4 can present challenges, but understanding and addressing common issues and implementing the most useful tips for your advantage will help you make the most of this powerful analytics platform.